38 phase labels in chemical equations
Chapter 7 Write the formula and identify the phase for the product (s) and balance the following reaction. Na 2 SO 4 (aq) + CaCl 2 (aq) ---> Since this is a double replacement reaction we can write the formulas of the products by exchanging the cations and anions. When you do this remember to keep track of the individual charges on the cations and anions. End-of-Chapter Material - GitHub Pages Chemical equations can also be used to represent physical processes. Write a chemical reaction for the freezing of water, including the proper phase labels. Explain why 4Na (s) + 2Cl2(g) → 4NaCl (s) should not be considered a proper chemical equation. Explain why H2(g) + 1/2O2(g) → H2O (ℓ) should not be considered a proper chemical equation.
What are Chemical Equations? Detailed Explanation, Examples The reactants and the products (for which the chemical formulae are written in chemical equations) can be separated by one of the following four symbols. In order to describe a net forward reaction, the symbol '→' is used. In order to describe a state of chemical equilibrium, the symbol '⇌' is used.

Phase labels in chemical equations
Phase Diagram | Explanation, Definition, Summary & Facts The first curve line (A, T) separated the solid and vapour phase, second curve line (T, B) separates the solid and liquid phase whereas third curve (T, C) separates the liquid and vapour phases of a substance (Fig. 1). Phase Rule - Teaching Phase Equilibria The system is entirely composed of H 2 O, so there is only one component present.; The phases present represent three states of matter: liquid (water), solid (ice), and vapor (steam). All have distinct physical properties (e.g. density, structure--or lack of, etc.) and chemical properties (e.g. Δ G formation, molar volume etc.) so they must be considered distinct phases. Solved 1. Write balanced chemical equations using proper | Chegg.com 1. Write balanced chemical equations using proper phase labels for these reactions: (you may also handwrite in the equations) a) Iron metal with oxygen gas to produce solid iron (III) oxide, also known as rust.
Phase labels in chemical equations. 6.3 Acid-Base Reactions - CHEM 1114 - Introduction to Chemistry The process represented by this equation confirms that hydrogen chloride is an acid. When dissolved in water, H 3 O + ions are produced by a chemical reaction in which H + ions are transferred from HCl molecules to H 2 O molecules ().. Figure 1. When hydrogen chloride gas dissolves in water, (a) it reacts as an acid, transferring protons to water molecules to yield (b) hydronium ions (and ... Definition of dissolve and the state label (aq) in chemical equations C O X 2 ( a q) would imply dissolved carbon dioxide in water (i.e.,to our eyes it is a single phase, just like an unopened bottle of coke). B r X 2 ( a q) would imply homogeneous solution of liquid bromine in water. N a C l ( a q): Salt dissolved in water. A colloid is a heterogeneous phase. GCSE CHEMISTRY - What are State Symbols? - (s) - (l) - (g) - (aq ... 4 Li (s) + O 2 (g) 2 Li 2 O (s) The state symbols in brackets show the physical state of. the substance at the reaction temperature. Solid (s), liquid (l), gas (g), or dissolved in water (aq). aq is called aqueous which comes. from the Latin word aqua meaning water. If you do not know the state of a substance. chemical equation | Yeah Chemistry Chemical reactions are represented by chemical equation, which identify reactants and products. Formulas of the reactants appear on the left side of the equation; those of products are written on the right. In many cases it is useful to indicate the state or phases of the substance in an equation.You use the following phase labels: (g) = gas , (l) = liquid , (s) = solid , (aq) = water solution ...
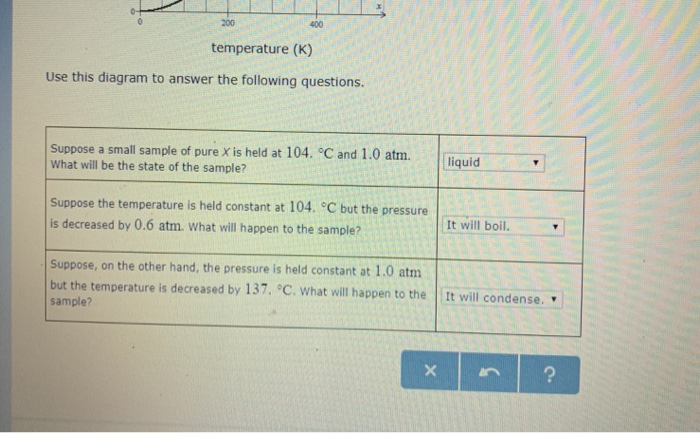
Chemical Equations - GitHub Pages It is not uncommon to include a phase label with each formula— (s) for solid, (ℓ) for liquid, (g) for gas, and (aq) for a substance dissolved in water, also known as an aqueous solution. If we included phase labels for the reactants and products, under normal environmental conditions, the reaction would be as follows: H2(g) + O2(g) → H2O (ℓ) Note Chapter 4 Section E Neutralization Reactions - PEOI Neutralization reactions are one type of chemical reaction that proceeds even if one reactant is not in the aqueous phase. For example, the chemical reaction between HCl(aq) and Fe(OH) 3 (s) still proceeds according to the equation 3HCl(aq) +Fe(OH) 3 (s) --> 3H 2 O(l) +FeCl 3 (aq) even though Fe(OH) 3 is not soluble. When one realizes that Fe(OH) 3 (s) is a component of rust, this explains why ... Phase Diagrams - Chemistry - University of Hawaiʻi Using the phase diagram for water given in [link], determine the state of water at the following temperatures and pressures: (a) −10 °C and 50 kPa (b) 25 °C and 90 kPa (c) 50 °C and 40 kPa (d) 80 °C and 5 kPa (e) −10 °C and 0.3 kPa (f) 50 °C and 0.3 kPa Solution Chapter 5 - Chemical Reactions and Equations - CHE 105/110 ... Many chemical equations also include phase labels for the substances: (s) for solid, (ℓ) for liquid, (g) for gas, and (aq) for aqueous (i.e., dissolved in water). Special conditions, such as temperature, may also be listed above the arrow. For example, 2NaHCO3 (s) − →−200°C Na2CO3 (s) +CO2(g) +H2O(ℓ) Key Takeaways
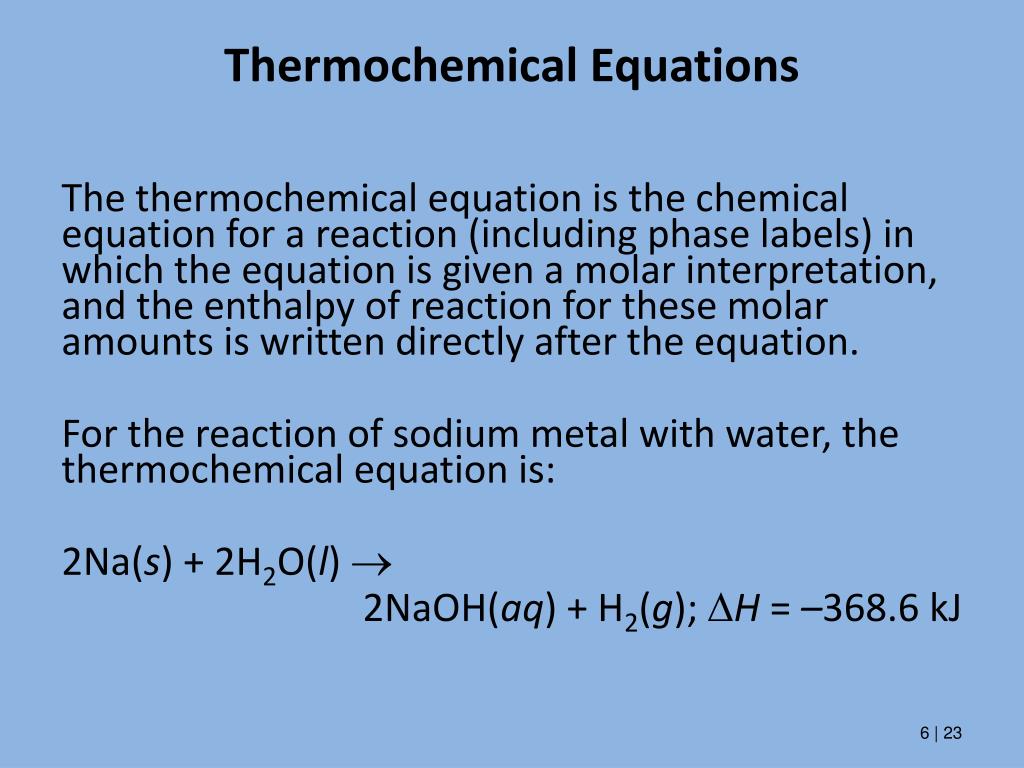
Solved 1. Write a balanced thermochemical equation with | Chegg.com Question: 1. Write a balanced thermochemical equation with phase labels for the Haber process with the heat energy as part of the equation. (3 pts) 2. What is the theoretical yield of ammonia (in grams) if 16.55 grams of nitrogen gas and 10.15 grams of hydrogen gas are allowed to react? (9 pts) 3. End-of-Chapter Material - Introductory Chemistry - 1st Canadian Edition Chemical equations can also be used to represent physical processes. Write a chemical reaction for the freezing of water, including the proper phase labels. Explain why 4Na (s) + 2Cl 2 (g) → 4NaCl (s) should not be considered a proper chemical equation. Explain why H 2 (g) + ½O 2 (g) → H 2 O (ℓ) should not be considered a proper chemical equation. 3 Steps for Balancing Chemical Equations - ThoughtCo To do this, you need to be familiar with the properties of various compounds or you need to be told what the phases are for the chemicals in the reaction. Oxides are solids, hydrogen forms a diatomic gas, tin is a solid, and the term ' water vapor ' indicates that water is in the gas phase: SnO 2 (s) + 2 H 2 (g) → Sn (s) + 2 H 2 O (g) Phase Diagrams - Purdue University Phase Diagrams. The figure below shows an example of a phase diagram, which summarizes the effect of temperature and pressure on a substance in a closed container. Every point in this diagram represents a possible combination of temperature and pressure for the system. The diagram is divided into three areas, which represent the solid, liquid ...
Phase diagram - Wikipedia A phase diagram in physical chemistry, engineering, mineralogy, and materials science is a type of chart used to show conditions (pressure, temperature, volume, etc.) at which thermodynamically distinct phases (such as solid, liquid or gaseous states) occur and coexist at equilibrium . Contents 1 Overview 2 Types 2.1 2-dimensional diagrams
Phases in chemical reactions | StudyPug The phase can affect how reactive a substance is, but changing phase (a physical change) is not the same as changing the substance (a chemical change). A fully detailed chemical equation will show the state (or phase) of matter that the atoms or molecules are in. These states are: Solid, given the symbol (s) Liquid, given the symbol (l)

Phase_Diagram_WorksheetL1 - Phase Diagram Worksheet For each of the questions on this worksheet ...
Symbols in Chemical Equations - Harper College Symbols in Chemical Equations. Symbol: Meaning + used to separate one reactant or product from another used to separate the reactants from the products - it is pronounced "yields" or "produces" when the equation is read used when the reaction can proceed in both directions - this is called an equilibrium arrow and will be used later in the ...
The Chemical Equation - Introductory Chemistry - 1st Canadian Edition Write and balance the chemical equation that represents nitrogen and hydrogen reacting to produce ammonia, NH 3. Answer N 2 + 3H 2 → 2NH 3 Many chemical equations also include phase labels for the substances: (s) for solid, (ℓ) for liquid, (g) for gas, and (aq) for aqueous (i.e., dissolved in water).
Phase Definition and Examples - ThoughtCo In chemistry and physics, a phase is a physically distinctive form of matter, such as a solid, liquid, gas, or plasma. A phase of matter is characterized by having relatively uniform chemical and physical properties. Phases are different from states of matter.
Phase Labels - YouTube Clark College Tutoring and Writing Center tutors Kevin Martin and Joey Smokey explain the usage of phase labels in chemical reactions such as (s), (l), (g), ...
Conventions for Writing Chemical Equations - Arrows, Phases ... presents: Conventions for Writing Chemical Equations including Arrows, Phases, Coefficients, Reactants, Products and moreTired...
5.1 The Chemical Equation - Introductory Chemistry - NSCC Many chemical equations also include phase labels for the substances: (s) for solid, (ℓ) for liquid, (g) for gas, and (aq) for aqueous (i.e., dissolved in water). Special conditions, such as temperature, may also be listed above the arrow. For example, 2 NaHCO3(s) →200°C Na2CO3(s) + CO2(g) + H2O (ℓ) Key Takeaways
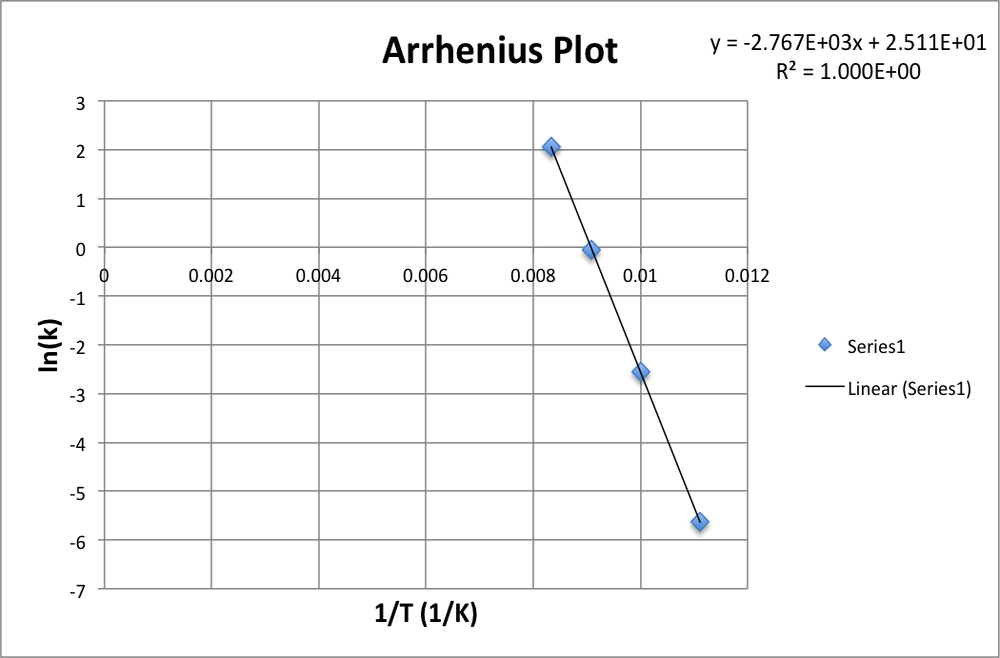



Post a Comment for "38 phase labels in chemical equations"